Guitar Joystick
August 9, 2025
Introduction
Recently I was really wanting to play a game of Frogger, but with inflation hitting hard I figured buying a joystick would be too expensive. I decided I could make my own using a guitar and an ESP32 board. Each note played on the guitar has its frequency calculated, translated into a MIDI note, and passed into the userland Linux kernel joystick driver of a PC.
Related Projects @mikekohn.net
Video
YouTube: https://youtu.be/Xjy8zHOBsSA?si=VUOm2HCJ7kQjns4o
Explanation
This project started out with a project I worked on a few years ago but kind of never really finished: MIDI guitar. That project would take a .wav file and using DCT calculate all the frequencies and output MIDI data into a .mid file so it can be played back. It was pretty clunky, but just needed some polish. That code was cleaned up and dropped it into an ESP32. It worked pretty decent, but was too slow.
Next step was to try something simpler. The sound data is represented by 16 bit signed numbers (-560 to 560). A single sound wave starts when the data goes from negative to positive, continues as the data goes positive to negative, and ends when the data goes from negative to positive again. Counting how many times the sound data does that over a time period can be used to calculate frequency. Seems to work pretty okay, but would fail obviously if multiple notes were being played at the same time.
The ESP32 code is running a timer interrupt gathering around 20,000 samples a second. During the interrupt it gets an audio sample and fills up a queue of 6,000 bytes. Every time the queue fills up by 1/2, the frequency is calculated which means the joystick update rate is about 3.3 times a second. The frequency is converted into a MIDI note which is transferred over UART to the PC. The PC listens for notes and sends it into theLinux kernel joystick driver using /dev/uinput (userland device driver for user input).
There are lots of parameters that have to be tuned to make this work: ADC samples per second, amplitude threshold on the guitar (ignoring quiet input from the guitar that could be noise), how many waves to read in to calculate the frequency, etc. The more waves, the more latency on each guitar note while the less waves might calculate the wrong frequency.
Conversion from frequency to MIDI note is being done in the Notes.cpp object. Since the guitar being used is tuned down 1/2 step, the notes being used for the joystick are:
[466.16 Hz] 70 - Bb4 UP
[391.99 Hz] 67 - G4 RIGHT
[349.23 Hz] 65 - F4 LEFT
[277.18 Hz] 61 - Db4 DOWN
udev
The code for doing user-land joystick is in the uinput/ directory. To start it up the following command is used:
sudo ./joydev /dev/ttyUSB1
ttyUSB1 may need to be replaced with the actual UART device being used.
Pictures
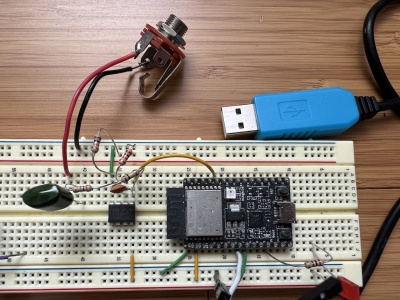
Above is a picture of the breadboard with the ESP32 and opamp circuit. The blue USB cable is a USB-UART adapter and is connected to pins 6/7 (RX/TX) of the ESP32 board.
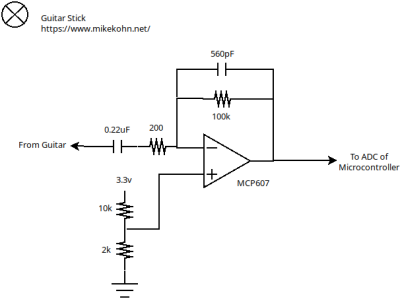
Above is a schematic of just the opamp part of the circuit. This is used to raise the voltage of the guitar signal center it around the reference voltage of the ADC peripheral in the ESP32.
Source Code
git clone https://github.com/mikeakohn/midi_guitar.git
Copyright 1997-2026 - Michael Kohn